How strong is my password? Am I secure against cyber-attacks?
The Evolution of Authentication Methods

With the evolution of the digital platforms, services, and digital devices, such as social media, online banking, mail services, e-commerce, mobiles, and computers, in addition to the critical information it holds, security measures to protect and identify who is allowed to access the information hosted on them becomes mandatory.
What is Authentication
Authentication is the act of validating and identifying who is allowed to access this platform/device and not the other by identifying and validating a certain type of associated credentials against a registered database such as a username and password.
What is called credentials, is being treated now and named as digital Identity, which reflects your image and holds your reputation in the digital world.
Failing in protecting the access to the systems you are using, puts the information and data hosted on them in danger of being leaked, accessed by unauthorised persons, who might use that information to do harm, to yourself, family, friends, or even businesses. İn addition to that, failing to protect your credentials/digital identity puts you in danger of being a victim of identity theft, which leads to financial, reputational risks, and might expose you to some juridical acts.
Therefore, having a robust and strong authentication mechanism to validate and verify your digital identity is a critical process for all service providers where they keep investing in developing better authentication systems.
Types of Authentication
Authentication techniques are built following three characteristics, where each one of them has its own pros and cons, and where the decision on which one to select should be taken based on trade-off among security, ease of use, and ease of administration. Authentication types can be implemented alone or in combination. To strengthen the authentication process, where multilayer of different types of authentication provides better protection.
- What the user knows—knowledge-based authentication (e.g., password, PIN, passcode)
- Password authentication: This is the most familiar authentication method which all of us are familiar with. where to log onto a network service, platform, or computer, you enter a user account name and the associated password. while to have minimal secure access, passwords must be “Strong” which means built of a combination of alphanumeric characters and symbols, hard to guess, long enough to not be cracked easily, or can be represented by a passphrase, which means a sentence built from many words. This authentication method is vulnerable to a password “cracker” technique and is considered the weakest methodology, while it is user friendly and easy to apply.[Text Wrapping Break]
-What the user has—possession-based authentication (e.g., memory card and smart card, tokens, device)
- Smart card authentication: Smart cards are credit card-sized devices that hold a small computer chip, that stores encrypted security keys in addition to other personal information used to identify the person holding this card and authenticate him or her to the system. This type of authentication requires you to physically insert/slide/tape the card into or through a reader where it requires to enter a personal identifier number to confirm your ID, this is typically similar to any Bank ATM card. This type of authentication is considered stronger than passwords, as it requires physical possession of the card and the user should know the PIN.
-What the user is—biometric-based authentication: physiological (e.g., fingerprint) or behavioral (e.g., keyboard dynamics) characteristics
- Certificate-based authentication: Certificate-based authentication technologies identify users, machines, or devices by using digital certificates, which is an electronic document based on the idea of a driver’s license or a passport, and it contains the digital identity of a user including a public key,
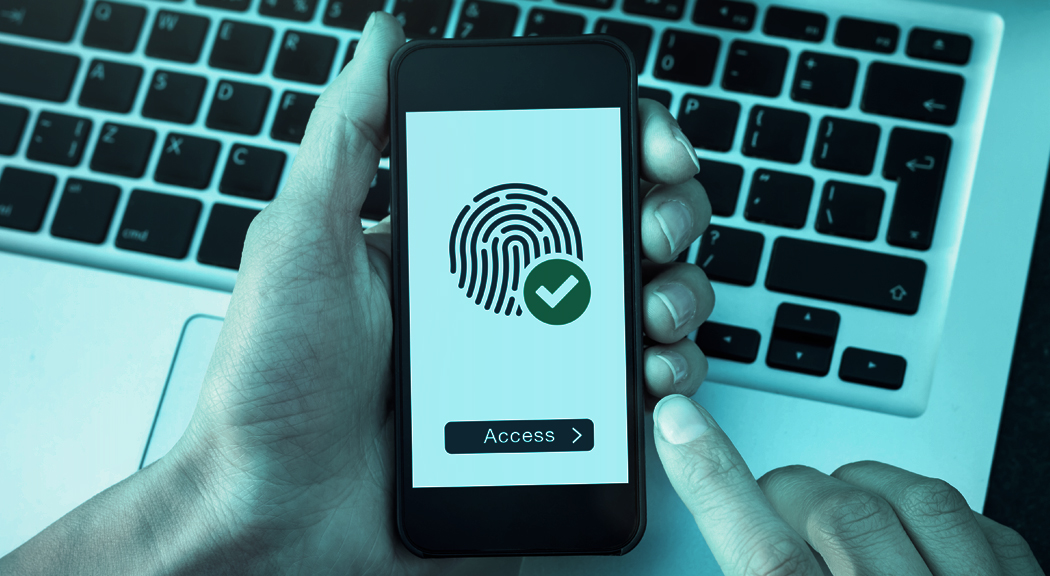
- Biometric authentication: a high-level authentication method is the biometric authentication that requires and involves the use of human biological traits and characteristics such as fingerprints, voice, face traits, Eyes, retinal, and iris. Those patterns are mainly unique and different for each one of us, hence have a high level of security. Such an authentication method requires expensive equipment to be able to read and detect biometric details, in addition to other advantages over the smart card and password, it does not require the user to carry any device or to remember a code.
All the type of authentication we have mentioned above, do have their pros and cons while implementing a high-level authentication level requires a combination of two or more factors (type of Authentication), hence the name “Multi-Factor Authentication” where the system challenges you against more than one factor to authenticate and validate your identity, while researchers are working to enhance and move to a futuristic approach, most of us start using and experiencing in a way,”Passwordless Authentication”. In an easier explanation, it means any method of verifying your digital identity without requiring you to provide a password.
Password-protected data
Nowadays, Having an account, protected with a password starts to give an impression of not being protected at all, since there is a lot of tools and attacks like spray attack, brute force, dictionary attacks, phishing and social engineering attacks with an intention to break and steal users passwords and accounts, without neglecting the bad relation between us as human being and the password itself, such as, writing down passwords, creating weak passwords, memorising complex password, in addition to reusing the same passwords on all accounts and platforms we have.
Hence, a new measure and approaches were taken by the researchers to build up, enhance and enforce authentication protocols and architecture, by adding new techniques and verification methods to identify and verify that the user who is accessing a certain account is the actual person and not someone who pretends to be that person.
Authentication without passwords: is it secure?
In this way, your Identity can be verified by using an alternative factor like a proof of possession factor (mobile authenticator apps, hardware token, one-time password OTP), biometrics, or even device certificates.
You are probably using passwordless authentication already by verifying your ID by logging in using FaceID on your iPhone, fingerprint authentication on Android, and logging into your laptop via Windows Hello, or even you access your bank account after receiving the OPT code to your mobile phone, or the push notifications you receive on your phone to approve a number shown on the screen or even the verification message you receives from Gmail while trying to sign in using a new device.
All these are enhancement types of security and verification methods, as it requires the user's interaction to verify his identity, either through physical presence and the ability to match verification numbers between the carried device and the platform the user is trying to access.
Yes, some if not most of these authentication types were mentioned above, but why is passwordless authentication gaining traction?
Passwordless authentication has gained traction because of its significant benefits in security and usability, including:
- Threat-resistant login options: No passwords to type, the likelihood of being phished is reduced.
- Visibility and control for admins: Admins control the security of their org and gain visibility into the specific factors in use per user.
- Scalability: Delivering a passwordless experience through factors that end-users already possess, such as their mobile device (biometrics and mobile authenticator apps), or their laptop (i.e. Windows Hello and fingerprint on MacOS) means easier scalability for users within your workforce and customer base.
- A great user experience: Users no longer need to remember and update complex password combinations.
After having gone through different types of authentication methods and clarifying the pros and cons of each one of them? Which one you are using to access your device, social media accounts, business email?
If you are still relying on using a password, it is the time to consider a different or combination of authentication methods.
@2x.png)